What Kind of Solid Is Crystalline Boron B
Ionic Bond Definition Properties Examples Uses. It is a network solid a lattice of many covalent bonds similar to a diamond except that it is black rather than transparent.

Pin On Chemistry Notes Jee Neet
Amorphous solid is a solid with considerable disorder in its structure as in common glass or rubber.

. Please explain the meaning of this statement above is the image of crystalline ceB2O3 from Wikipedia. Chemical properties of boron. Pair distribution function analysis revealed a drastic decreas.
They have a sharp melting point. Boron is a nonmetallic element existing as a dark brown to black amorphous powder or as an extremely hard usually jet-black to silver-gray brittle lustrous metallike crystalline solid it is a network solid a lattice of many covalent bonds like diamond except that it is black rather than transparent. Is boron a gas or metal.
Boron is a non-metallic element that forms a dark brown to black amorphous powder or a very hard metallic crystalline solid usually jet-black to silver-gray brittle lustrous metallike. What kind of solid is crystalline boron B. The forces of chemical bonding causes this repetition.
Identify the type of crystalline solid metallic network covalent ionic. Boron B Silicon Dioxide SiO 2 etc. Borax is converted into crystalline boron by the following steps.
A crystal lattice is a repeating pattern of mathematical points that extends throughout space. Classified as a metalloid Boron is a solid at room temperature. The interesting feature of this structure is that the boron atoms are forming half-bonds by sharing one electron instead of the usual two electrons in a covalent bond.
In special circumstances boron can also be synthesized in the form of its α-tetragonal and γ-orthorhombic allotropes. Crystalline solids have well-defined edges and faces. The structure of crystalline ceB2O3 consists of ceBO4 tetrahedra two sets of which form two types of interconnected spiral chains three ceB-O bonds are equivalent but the fourth one is somewhat longer.
Boron B exists as either a brown powder or a crystalline silvery black solid. It is a metalloid and has both metal and non metal properties. Boron is electron-deficient possessing a vacant p-orbital.
Boron is a chemical element with symbol B and atomic number 5. Both of these compounds that are clearly molecular or molecular and last but not least boron can bond. Properties of Crystalline Solids.
B o r a x. Boron noun The chemical element symbol B with an atomic number of 5 which is a metalloid. Indicate the type of solid molecular metallic ionic or covalent-network for each compound.
What kind of solid has a regular and repeating arrangement of atoms. We synthesized a palladiumrutheniumboron PdRuB solid-solution ternary alloy. The crystalline form of borax has.
Elemental mappings confirmed successful alloying of B with PdRu body without changing the particle sizes demonstrating the first discovery of this ternary alloy. Boron Crystal Structure. A possible crystal structure of Boron is rhombohedral structure.
What kind of solid is crystalline boron B. Graphite is covalent crystalline solid. All four phases are stable at ambient conditions and β-rhombohedral is the most common and stable.
A white or graygrey crystalline salt with a slight alkaline taste used as a flux in soldering metals making enamels fixing colorscolours on porcelain and as a soap etc. There are so many essential properties of crystalline solids. Crystalline solids are composed of small crystals having a specific geometrical shape.
The basic unit for the crystalline structure of boron is a B 12 icosahedron with at each of the 12 vertices a boron atom bonded to five other atoms. Borons most common use is in compounds such as Boric acid and Borax which are used in antiseptics washing powders and glazes. H C l C.
View solution View more. Boron can be prepared in several crystalline and amorphous forms. Total number of sigma bonds formed by all the boron atoms in borax is.
Crystalline boron is a very hard black material with a melting point of above 2000 C. Correct option is A In first step Boric acid is obtained by treating a hot concentrated solution of. Boron is a non metallic element and the only non-metal of the group 13 of the periodic table the elements.
They have a long-range of orders. Properties of boron Pure boron is a high melting solid diamagnetic substance melting point 2180 C which is either crystalline black or amorphous brown It is used as a semiconductor that conducts electricity at high temperatures like a metal. Well known crystalline forms are α-rhombohedral β-rhombohedral and β-tetragonal.
The factor that has the greatest effect on the melting point of a crystalline solid is the type of bonding among the particles. Um Its a non metal it can share and create Covalin bonds. Mindmap Cheatsheets.
View chapter Shortcuts Tips. Get Answer to any question just click a photo and upload the photo and get the answer completely free UPLOAD PHOTO AND GET THE ANSWER NOW. Is has the atomic number 5 in the periodic table and belongs in Group 13 its symbol is B.
It forms four major allotropes. In metals and in many other solids the atoms are arranged in regular arrays called crystals. α-rhombohedral and β-rhombohedral α-R and β-R γ-orthorhombic γ and β-tetragonal β-T.
Heat breaks the bonds that hold the particles together. Two amorphous forms one a finely divided powder and the other a glassy solid are also known. Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance scoring excellent marks in exams.
They have a regular arrangement of atoms ions and molecules in a three-dimensional pattern called a crystal lattice. For example the crystals of sugar and table salt etc. H C l A l.
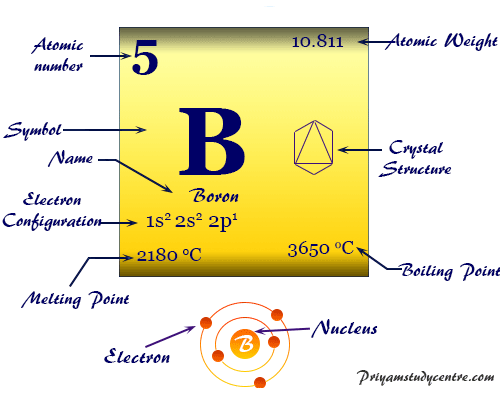
Boron Element Symbol Properties Preparation Uses Facts

Comments
Post a Comment